Eye Centre
- Home
- Eye Centre
-
Lasik
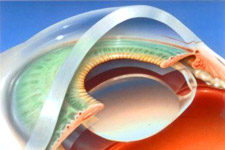
Lasik treatment is performed under local anaesthetic (just a few drops of eye-drop in each eye) and it is completely painless both during the surgery and in the post-operative stages. Except for rare cases, the operation is bilateral, i.e. performed on both eyes during the same operation. This allows a reduction of the recovery period and a better visual comfort during the post-operative stage.
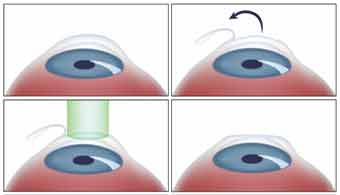
The first step of the operative procedure consists in the creation of a corneal flap (hinged flap) using a specific surgical instrument. The most common one is called microkeratome and it is a mechanical computerised instrument that uses a thin blade to create a flap.
To perform this critical phase we use the latest technology, called femtosecond laser. The femtosecond laser replaces the blade used to create the flap with a laser which guarantees more precision and a better flexibility of the incision. Moreover, with the use of the femtosecond laser the operation is safer and the risks are nearly reduced to zero.
During the second step of the operation an excimer laser corrects the visual disorder, remodelling the curvature of the cornea. It removes a larger quantity of tissue from the central area of the cornea in case of myopia, while in case of hyperopia it removes a larger quantity of tissue from the peripheral area.
The patient can go back to his everyday activities even the day after the surgery, except for some particular ones (sports that involve physical contact, swimming, make up).Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-
PRK
PRK surgery is performed under local anaesthetic (just a few drops of eye-drop in each eye) and is completely painless during the surgery.
Except for rare cases, the operation is bilateral, i.e. performed on both eyes during the same operation. This allows a reduction of the recovery period and a better visual comfort during the post-operative stage. The first step of the operation consists in the removal of the corneal epithelium with the help of a particular minimally invasive instrument used in microsurgery.
During the second step of the operation an excimer laser corrects the visual disorder, remodelling the curvature of the cornea. It removes a larger quantity of tissue from the central area of the cornea in case of myopia, while in case of hyperopia it removes a larger quantity of tissue from the peripheral area.
To finish, therapeutic and protective contact lenses are applied to help natural corneal epithelium healing.
After the operation the patient may feel a moderate pain that can last 1-2 days. After the third day the contact lenses are removed and the patient undergoes the first eye tests. At this stage eyesight is already pretty good and it allows to go back to your everyday activities, except for some particular ones (sports that involve physical contact, swimming, make up). Complete visual recovery gradually occurs in about one month.Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-

Phakic IOL Implant
In case of high myopia or hyperopia, when the laser surgery is contraindicated, it is possible to proceed with the implant of a soft contact lens (called phakic) placed either between the cornea and the iris or just behind the iris, by a small incision. In this way the natural crystalline and its accommodative capacity are preserved.
The operation is unilateral and is performed under local anaesthetic (just a few drops of anaesthetic eye-drop in the eyes) with a light sedation if necessary.
The recovery is very quick and painless, the patient can see straight after the surgery.
The patient can go back to his everyday activities even the day after the surgery, except for some particular ones (sports that involve physical contact, swimming, make up).Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-
Refractive Cataract Surgery
Refractive cataract surgery consists in the replacement of the opaque lens (cataract) with an artificial lens, optimised to correct the visual disorder. The operation is performed under local anaesthetic (just a few drops of anaesthetic eye-drop in the eyes) and it is completely painless. The surgery in unilateral, i.e. performed on a single eye per operation.
During the first step the opaque lens is removed by an instrument called phacoemulsification probe or by a specific laser. The natural membrane that wraps up the lens is kept intact.
During the second step an artificial lens is implanted in the eye of the patient, replacing the natural lens previously removed. Nowadays a wide variety of lenses for refractive cataract surgery exists: monofocal lenses (optimising your sight at a certain distance), or multifocal lenses, that have to be implanted in both eyes to maximise the focus of close objects (to improve your vision in the distance and near and to correct presbyopia).
After the surgery the patient will not feel any pain. Visual recovery is fast. The patient will need one day in order to properly focus far objects in case of both monofocal and multifocal lenses implant, while there will be a gradual adjustment to focus close objects (from a minimum of two weeks to a maximum of a few months from the implant of the second lens).Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-
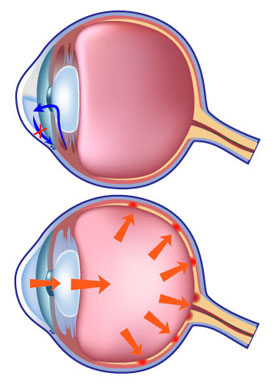
Glaucoma treatments
Surgical treatmentIn particular cases a special surgery that implants a small plastic “valve” is recommended. These “drainage implants” allow the outflow of the aqueous humour to be carried through the tissue of the bulb of the eye and to be redirected backwards, underneath the conjunctiva, in order to decrease the intraocular pressure. It is an outpatient surgery performed under local anaesthetic (a few drops of eye-drop). This kind of operation entails a remarkable decrease of the post-operative complications and the patient can go back home the same day of the surgery. After the operation the patient may feel a foreign body in the eye that gradually fades away. No pain at all is felt, neither during the surgery nor after it.
Parasurgical treatment
Modern ophthalmic lasers allow to perform effective surgeries for the treatment of glaucoma. In some cases it is possible to perform a laser treatment without the need for incisions. In some other cases an eye incision is necessary to create a new drainage duct.
Pharmacological treatment
Nowadays we have a wide variety of medications available that can lower intraocular pressure, so we have to choose the best treatment for each patient. We have to start the treatment with the medication that lowers and keeps intraocular pressure to the right value and that, at the same time, is well tolerated by the patient (age, job, other eye or systemic pathologies, dosage).
Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-
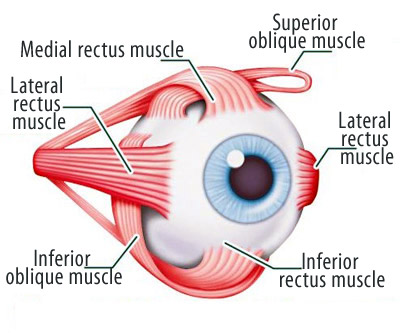
Strabismus treatment
Strabismus surgeryStrabismus surgery can be necessary for different reasons:
- Efficiency recovery, for example in case of exotropia (divergent squint), helping to restore normal binocular view.
- Correction of diplopia and of ocular torticollis are common goals of the surgery in case of paretic strabismus. Sometimes, in these cases, the results are limited to the primary position of the eyes (aligned gaze ahead).
- Aesthetic function: both in children and in adults, suffering from strabismus can be the cause of insecurity, psychological problems and difficulty in relationships with other people.
Pre-operative examinations consist in several tests in order to simulate the results of the operation with prism lenses and to predict aesthetic and sensorial results.
The surgery operates on one or more extraocular muscles, i.e. the small muscles that control the movement of the eye in the different directions.
The most common performed surgeries are two: recession, that weakens the muscles, moving its insertion posteriorly in the sclera, and resection, that strengthens the muscle, removing a part of it and tightening it.
It is possible to perform the surgery on one or more muscles, at the same time or in two different operations.
In young people and adults the surgery is usually performed under local anaesthetic, in order to get a precious collaboration with the patient during the surgery and the advantage of a one-day procedure.
After surgery the patient should expect swollen and red eyes; these effects fade away in about 3 weeks. It is possible to go back to usual everyday activities within 48 hours from the surgery.Use the arrows to browse the different treatments
-
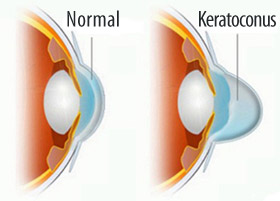
Cross-linking treatment
In case of cornea affected by keratoconus at early stages, when the vision condition is not seriously compromised yet, it is possible to carry out a new laser treatment called cross-linking.
The treatment consists in the application of a solution called Riboflavin on the eye. The following illumination with UV-A light (370nm), emitted by a specific device, activates oxygen free radicals that produce a change in the collagen structure. This change strengthens the corneal tissue, preventing it from further deformations. The treatment is useful to stop worsening in the patient conditions.
The FIRST STEP, called imbibition, can be performed with two different techniques:
- traditional procedure: the corneal epithelium is removed with the help of a specific minimallyinvasive instrument used in microsurgery. Once applied on the cornea, Riboflavin is absorbed. Contact lenses are then applied.
- femtosecond laser procedure: the femtosecond laser prevents from removing the corneal epithelium before the application of the Riboflavin.
The SECOND STEP, called activation, consists in the illumination of the Riboflavin with a low-intensity ultraviolet light (UV-A).
In case of the traditional procedure the patient may feel a moderate pain for 1-2 days. After the third day the contact lenses will be removed.
In case of surgery with the femtosecond laser the post-operative phase is completely painless and it is not necessary to apply contact lenses.Use the arrows to browse the different treatments